Monitoring the Metrics that Matter
Quantifying the impact of strategic initiatives is a critical aspect of success in today's digital age. It’s a task that is becoming increasingly complex, yet more vital than ever before.

Sustainability is at a critical turning point. New regulations will make companies more accountable and comparable in terms of their environmental impact. Downstream customers and consumers are increasingly concerned about climate change’s impact on both people and the economy. In addition, the troubled position of voluntary carbon credit markets has reduced their attractiveness to offset emissions. In this landscape, companies need to seriously reduce their Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions to address one of the central challenges of sustainability.
But the pressure to deliver financial performance looms large—especially given the uncertain economic climate—creating tension between short-term financial performance and long-term investments in sustainability.
Sustainability is an externally-driven requirement. For most companies, it was not baked into their financials or operating model. Simply put, it was not the plan—and certainly not the plan in an uncertain economic climate with inflation and earnings pressure still at play.
And for most companies, the near-term risks are likely modest. Commercial pressure from customers or competitors has not sufficiently formed and reputational risk has been more applicable to firms that have overstated gains.
So allocating capital now to a future set of risks, especially if funds are already allocated to meet regulatory requirements, may seem unnecessary.
But two factors should influence near-term investment decisions: the risk environment is expected to materially change in 2025; and sustainability programs will take time to develop and perform. Looking at the risk assessment matrices for 2023-2025 and 2025-2030 below, one can see that risks are muted in the near-term, barring the risks from carbon offset overstatements. Isolating just two, reputational and financial, shows how risks will increase in both likelihood and impact in the 2025-2030 timeframe.
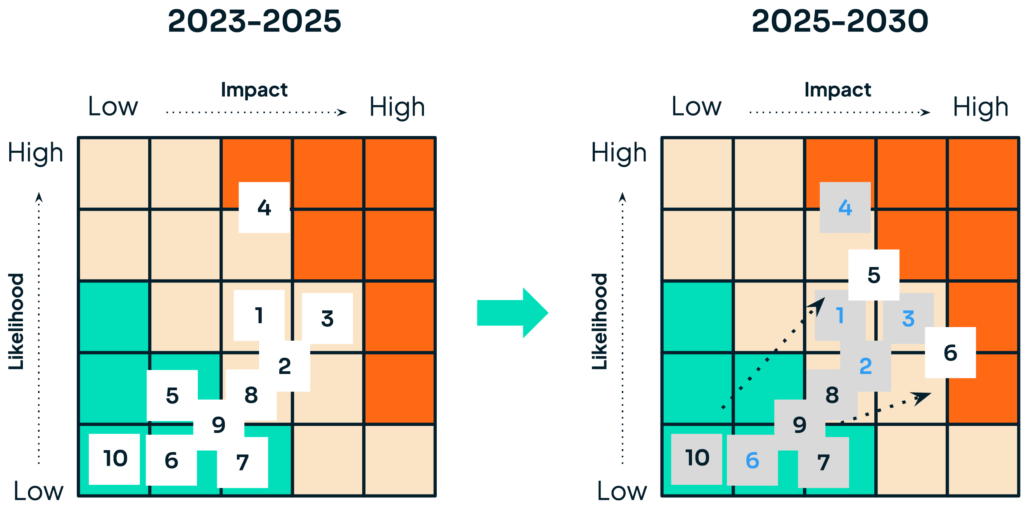
The challenge is that it will take time to make sufficient progress in sustainability to mitigate foreseeable reputational and financial risk starting in 2025. The concern for those who defer funding is that they will likely overspend once the risks are seen, especially if they start to see customers move their spending elsewhere.
If this plays out, companies will be forced to invest in programs that are not yet mature and not able to efficiently deliver results. That will result in a lot of money wasted on projects that can’t deliver the kind of progress needed.
Resource allocation will prove to be complex, especially in the near term. The need to closely manage costs, fund new sustainability reporting requirements, and invest in a program tasked with delivering sustainability performance will all pull against each other.
A way to balance these competing forces is to seed investment in a sustainability program in Year 1 to get it on its feet, begin the learn and build process, and be able to show progress through reporting and the associated public comparability. This may lead many companies to look hard at Scope 2 emissions to reduce energy costs and at Scope 3 (which produces more than 70% of carbon emissions) at little direct cost, creating an early and efficient path to sustainability.
Once companies have reporting set up, they can balance financial and sustainability performance. This is done by relying on the sustainability program’s management and measurement tools, which can identify, measure, and implement initiatives that have dual benefits in terms of finances and sustainability. Additionally, companies can use various working capital funding mechanisms to closely manage the initiatives that are vital for sustainability even if their financial benefits aren’t immediately evident.
But the key concept remains: the tension between financial and sustainability performance is likely a permanent fixture for sustainability. This means companies will need to have the right sustainability management and measurement tools in place to consistently achieve a balance between financial and sustainability goals.

Download the one pager to learn how Metaimpact powers seamless coordination across internal teams, strategic partners, and customers with a secure, collaborative data platform purpose-built to align efforts around shared objectives, consolidate shared data to measure progress, and accelerate delivery of business outcomes.

Download the one pager to learn how Metaimpact enables corporate foundations to collaborate with grant recipients on funded initiatives, give grantees the opportunity to connect, and demonstrate the collective impact of their philanthropic endeavors.

Download the ebook to learn how your organization can go beyond reporting and put a sustainability program in place that drives real progress.

Download the one pager to learn how Metaimpact equips visionary leaders of multi-stakeholder efforts with the tools to define shared goals, drive collective action, and measure meaningful progress.

Quantifying the impact of strategic initiatives is a critical aspect of success in today's digital age. It’s a task that is becoming increasingly complex, yet more vital than ever before.

In order to use data more effectively, a different approach is needed—software that enables data storytelling.

Much of the world associates the metaverse with avatars and immersive VR experiences, which is key for consumers and some business applications, but this new computing paradigm offers a more foundational and transformative opportunity for the business world.

As data storytelling becomes a more integral part of business strategy, new opportunities will surface, valuable internal conversations will occur, and departments will become more aligned.
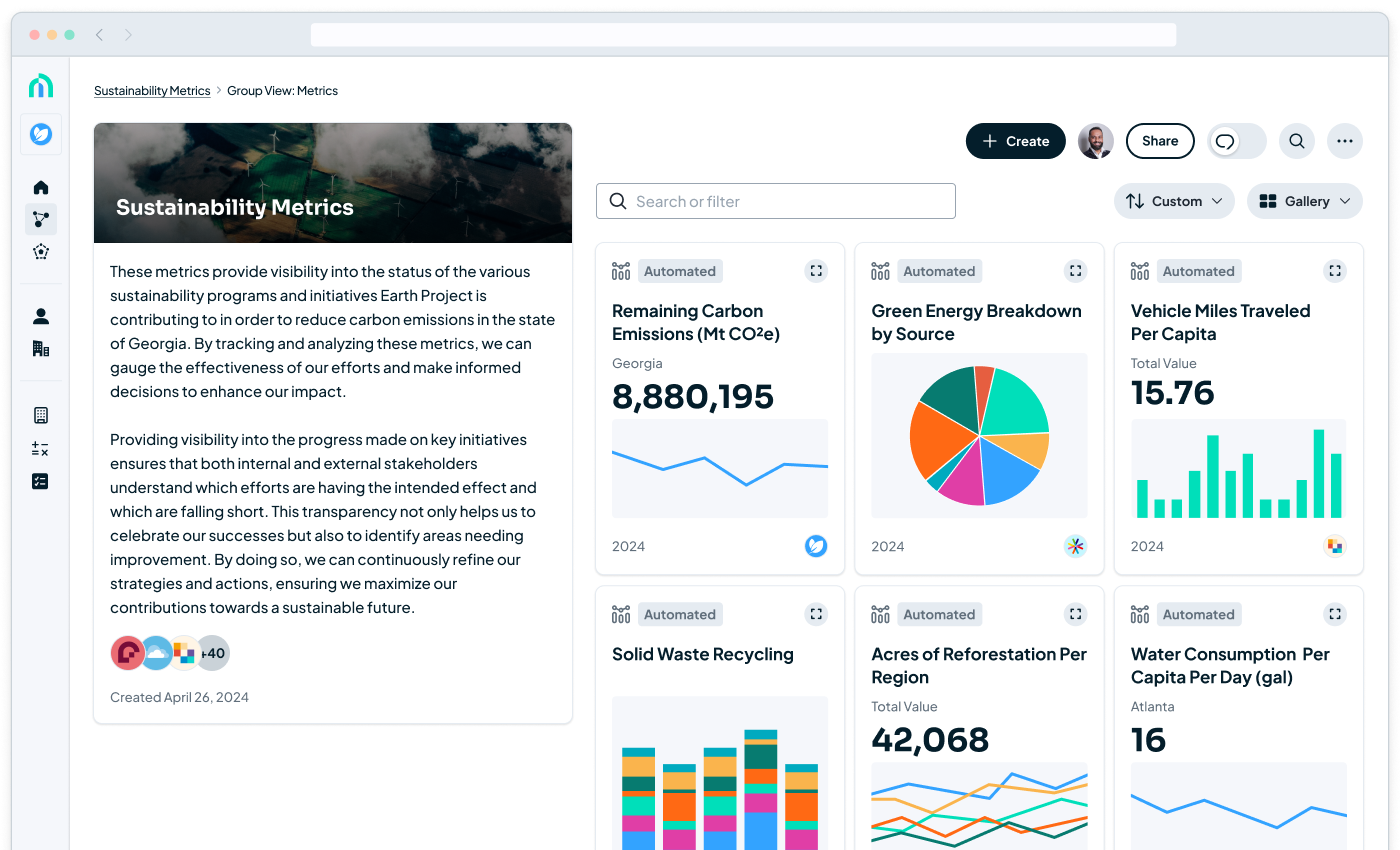
Request a demo to learn how Metaimpact helps organizations measure performance.